Tungsten Heat Sink Providing Exceptional Heat Dissipation for Electronics
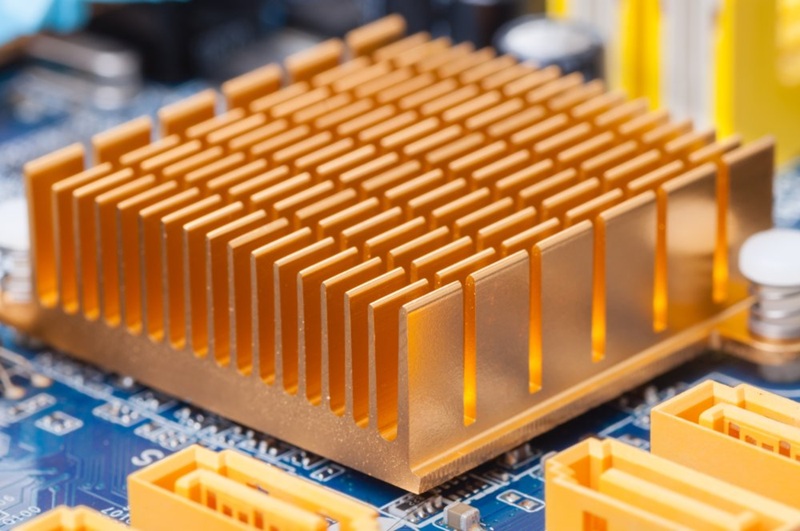
The Tungsten heat sink represents a pinnacle of thermal engineering, offering solutions to heat dissipation challenges that would overwhelm lesser materials. In observing the development of thermal management technologies, one cannot help but draw parallels to the adaptive strategies found throughout the natural world, where organisms have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to regulate temperature and maintain optimal operating conditions. The electronic devices that power our modern civilization face similar imperatives, requiring efficient pathways to channel unwanted thermal energy away from sensitive components before performance degrades or catastrophic failure occurs.
Understanding the Thermal Challenge
Electronic components generate heat as an inevitable consequence of their operation. As current flows through resistive elements and transistors switch states millions of times per second, electrical energy transforms into thermal energy. This heat, if left unmanaged, accumulates rapidly within the confined spaces of modern electronic assemblies. Temperature rises degrade semiconductor performance, accelerate aging processes, and ultimately lead to device failure. The Tungsten heat sink addresses this fundamental challenge through superior material properties and thoughtful engineering design.
The relationship between temperature and reliability follows well-established physical principles. For every 10-degree Celsius increase in operating temperature, the failure rate of electronic components approximately doubles. This sobering reality drives the continuous pursuit of more effective cooling solutions, particularly as power densities in modern electronics continue their upward trajectory.
Material Advantages in Thermal Applications
Tungsten brings several distinctive advantages to thermal management:
- Exceptional temperature tolerance with a melting point exceeding 3,400 degrees Celsius, providing substantial safety margins in high-temperature applications
- Consistent thermal performance across a wide temperature range, maintaining effectiveness where other materials degrade
- Superior thermal mass due to high density, enabling effective heat buffering and temperature stabilization
- Minimal thermal expansion reducing mechanical stress in multi-material assemblies
- Chemical stability resisting oxidation and corrosion in harsh operating environments
Singapore’s Tungsten heat sink industry has leveraged these properties to develop solutions for particularly demanding applications, where conventional cooling approaches prove inadequate. The combination of thermal conductivity and heat capacity creates a material uniquely suited to managing transient thermal loads whilst maintaining steady-state cooling performance.
Critical Applications and Industries
Tungsten heat sink finds essential roles across diverse technological domains. In telecommunications infrastructure, high-power amplifiers generating kilowatts of heat require robust thermal management to maintain signal integrity and prevent equipment damage. The aerospace sector relies upon tungsten’s reliability in applications where failure carries severe consequences, from satellite electronics enduring extreme thermal cycling to avionics systems operating in demanding environments.
Medical technology presents another crucial application area. Imaging systems, therapeutic lasers, and diagnostic equipment all depend upon precise temperature control to deliver consistent, accurate results. The Tungsten heat sink provides the thermal stability these sensitive instruments require, much as homeostatic mechanisms in living organisms maintain the narrow temperature ranges necessary for biological function.
Industrial laser systems, particularly those operating at high continuous power levels, benefit enormously from tungsten’s thermal properties. The material’s ability to absorb and dissipate intense heat whilst maintaining dimensional stability proves invaluable in these applications. Singapore’s Tungsten heat sink manufacturers have developed specialized designs optimized for laser cooling, incorporating features that enhance convective heat transfer whilst preserving the structural advantages tungsten provides.
Design Optimization and Performance Enhancement
Effective heat sink design requires more than simply selecting appropriate materials. The geometry of heat dissipating surfaces, the interface between heat source and sink, and the broader thermal pathway all influence overall performance. Engineers employ computational fluid dynamics and thermal modeling to optimize these factors, creating designs that extract maximum cooling capacity from available space and materials.
The surface finish of a Tungsten heat sink affects thermal interface resistance, the often-overlooked barrier to efficient heat transfer between component and cooling solution. Careful attention to surface preparation and the selection of appropriate thermal interface materials ensures that tungsten’s inherent advantages translate into real-world performance gains.
Fin design represents another crucial optimization opportunity. The spacing, height, and thickness of cooling fins must balance several competing factors: increased surface area for convection, adequate airflow between fins, and structural integrity. Too closely spaced fins restrict airflow; too widely spaced fins sacrifice surface area. The optimal configuration depends upon the specific cooling regime, whether natural convection, forced air, or liquid cooling.
Integration with Modern Cooling Systems
The Tungsten heat sink often forms part of a comprehensive thermal management system. In high-performance applications, tungsten may serve as the primary heat spreader, rapidly conducting heat away from concentrated sources before transferring thermal energy to secondary cooling mechanisms. This staged approach to thermal management mirrors the hierarchical strategies we observe in complex biological systems, where multiple mechanisms work in concert to maintain thermal equilibrium.
Hybrid cooling solutions combining tungsten heat sinks with heat pipes, vapor chambers, or liquid cooling loops offer exceptional performance for the most demanding applications. The thermal mass of tungsten provides buffering against thermal transients whilst other cooling technologies handle continuous heat removal. Singapore’s Tungsten heat sink developers have pioneered several such integrated approaches, demonstrating how thoughtful system design amplifies material advantages.
Conclusion
The evolution of thermal management technology continues apace, driven by relentless increases in electronic power density and performance demands. Throughout this progression, certain materials distinguish themselves through combinations of properties that address specific challenges with particular elegance. The Tungsten heat sink exemplifies this principle, offering thermal performance, temperature tolerance, and reliability that justify its selection for critical applications where failure is not an option, securing its position as an indispensable solution in advanced thermal management through the exceptional capabilities only a Tungsten heat sink can provide.





